In previous post, I showed about the LCD interfacing in 4-bit mode. The HD44780 allow the micro-processor to send the 8-bit data or command using an 4-bit interfacing. This process requires the microprocessor to send the 8-bit command or data twice over the 4-bit wire. The microprocessor send the higher nibble D4...D7 first, and then the lower nibble D0...D3. This technique saves the number of microprocessor digital output pins and circuit wiring. For more information about 4-bit LCD interfacing you can read this article.
 |
| Circuit Wiring On Bread Board |
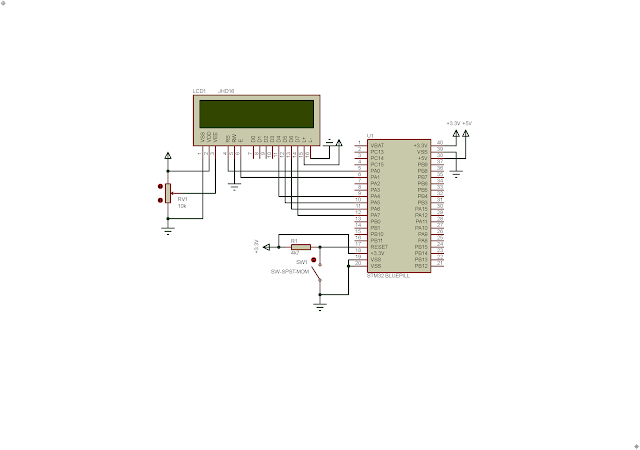
In this programming example, I use the lower byte of Port A. It's 16-bit wide. Where the LCD connections between the STM32F103C8R6 Blue Pill are,
- LCD Register Select (RS) connects to PA0,
- LCD Read or Write (R/W) connects to GND as the LCD just need to receive command or data,
- LCD Enable (EN) connects to PA1,
- LCD Data D0...D3 left unconnected or connects GND, while the LCD Data D4...D7 connects to the Blue Pill PA4...PA7.
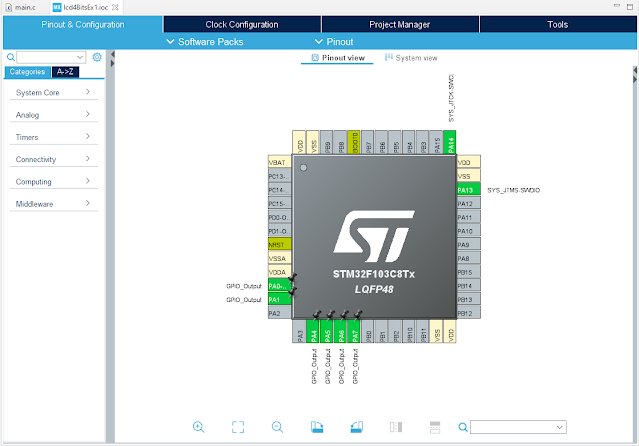
STM32CubeIDE Code Configuration Wizard allows the programmer to select any peripherals and system settings without writing code in C/C++ source file.
GPIO Selection |
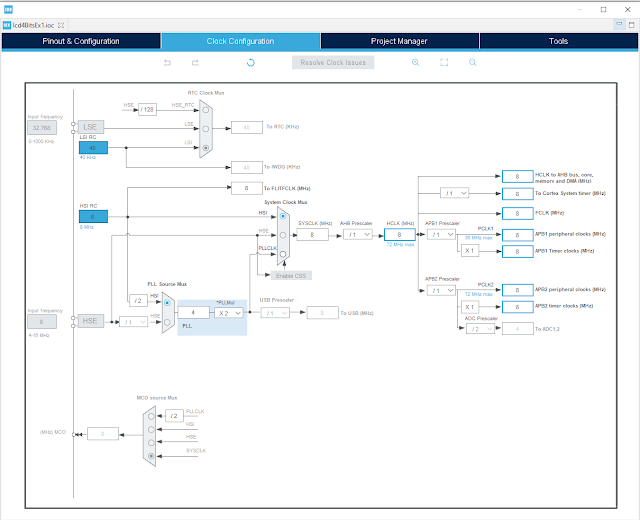
Clock Configuration |
 |
| Schematic |
JHD16 LCD Module Front |
JHD16 LCD Module Back |
The source source code is quite easy as it's similar to LCD interfacing in 8-bit mode.
I use C/C++ loop to create delay without using the STM32CubeIDE Hal_Delay function. However the delay time is not known.
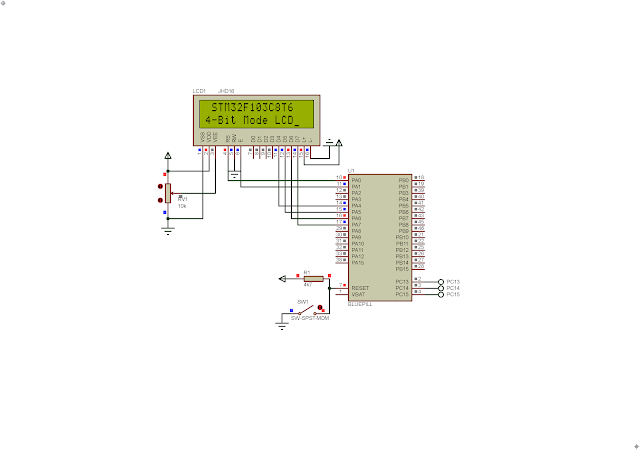 |
| Simulating Program In Proteus |
Click here to download its source file.


.jpg)
No comments:
Post a Comment