External interrupt is an external notification to the micro-controller. Usually, an external event (sense) such as logic changing, or edge triggering.
In ATMega32, there are three external interrupt source, INT0, INT1 and INT2. Each source locate at different pins.
- INT0 at PD2
- INT1 at PD3
- INT2 at PB2
- Low logic level
- Logic changing
- Falling edge
- Rising Edge
To program the interrupt, set up the code in the following step:
- Set the interrupt input pin as digital input
- Enable the interrupt for the corresponding input
- Enable the global interrupt control
- Keep your main program loop working
- Write the interrupt service routine to handle the corresponding interrupt
In ATMega32 the external interrupt is controlled by the GICR (General Interrupt Control Register).
| General Interrupt Control Register |
We enable any external interrupt by giving "1" to the source. For example, external interrupt 1 is enabled by setting INT1=1.
Interrupt flag contain the information about the state of any presenting interrupt. GIFR (General Interrupt Flage Register) store the status of external interrupts.
| GIFR (General Interrupt Flag Register) |
We can test any each external interrupt flag of this register to find the interrupt source. For example, we find INTF1=1, that mean that external interrupt INT1 is occur.
There are four modes of event (sense) the trigger the interrupt, as mention about. Those senses are controlled in the MCU Control Register (MCUCR).
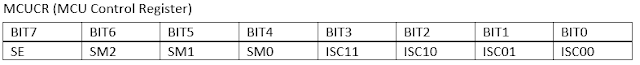 |
| MCUCR (MCU Control Register) |
The ISC11 and ISC10, are the interrupt sense control of INT1.
The ISC01 and ISC00, are the interrupt sense control of INT0
There four mode of sense as refers to the datasheet. By default, they sense Low to trigger interrupt.
The ISR locates at the interrupt vector. Each interrupt source has their own interrupt vector. For example INT0_vect is an interrupt vector for external interrupt 0.
In this example, I use all three external interrupt sources. The interrupt sense is logic low. So when I make any external interrupt pin low, it will generate the interrupt. The ISR is to toggle LED output each corresponding to the source.
 |
| Schematic and Simulation Diagram. We have external interrupt, INT0, INT1 and INT2 connect to its individual active low push button. Each interrupt toggles the corresponding output LEDs. |
Source code:
Click here to download this example.
If you want a standard PCB for ATMega32 micro-controller, you can order my AVR Microcontroller project from PCBWay with a reasonable price. Click here to get a free $5 credit for new account.
thankyou, it works perfactly
ReplyDeleteThanks you
DeletePORTB=(1<<2); and comment //PB2 USED FOR INT2 . How these two are related?
ReplyDelete