In this ARM programming example, I will use an earlier day character LCD to show text. This character LCD conventionally uses an HD44780 LCD controller manufactured by Hitachi. Currently there are a lot of low cost equivalent LCD controllers.
 |
| Blue Pill Experiment On Bread Board |
I will not write the details about this controller here because it's already explained in previous tutorial. But it uses the ATMega32 AVR micro-controller.
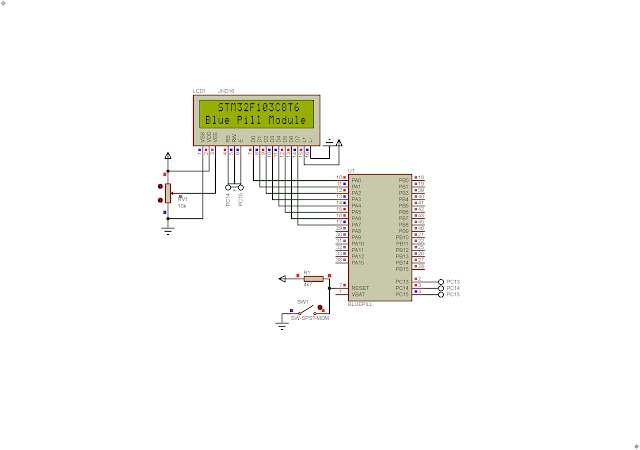 |
| Blue Pill Simulating Program Using Proteus VSM 8.15 |
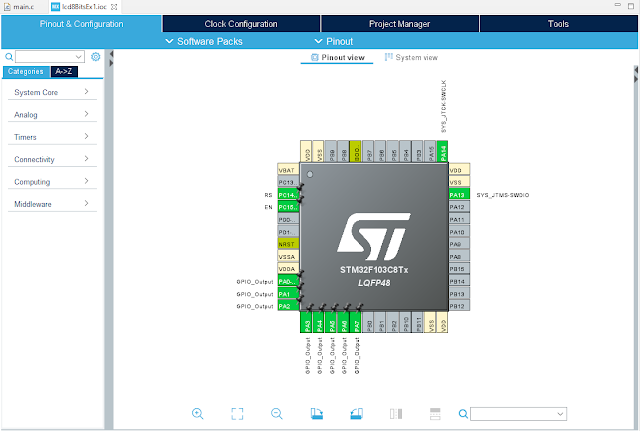
I use the lower nibble of Port A to send command or data to LCD module. PortA is a 16-bit bi-directional I/O. PC14 connects to LCD Register Select (RS) while PC15 connects to LCD En (Enable). As we just needs to send data or command to LCD module, the LCD Read/Write (R/W) just connect to GND.
GPIO Setting In Device Configuration Tool |
Without writing a legacy style C/C++ for ARM micro-controller, I use the Code Configuration Tool inside the STM32CubeIDE. It will generate C/C++ source code whenever we have finish all preferred setting on target MCU.
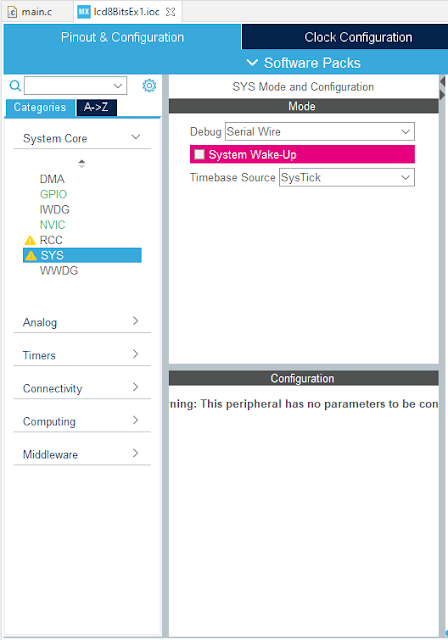 | |
| SYS Setting |
In SYS tab, I select Serial Wire as the debug interface with ST-LINK V2. The System Wake-Up check box must left unchecked to enable the PA0 as general purpose I/O.
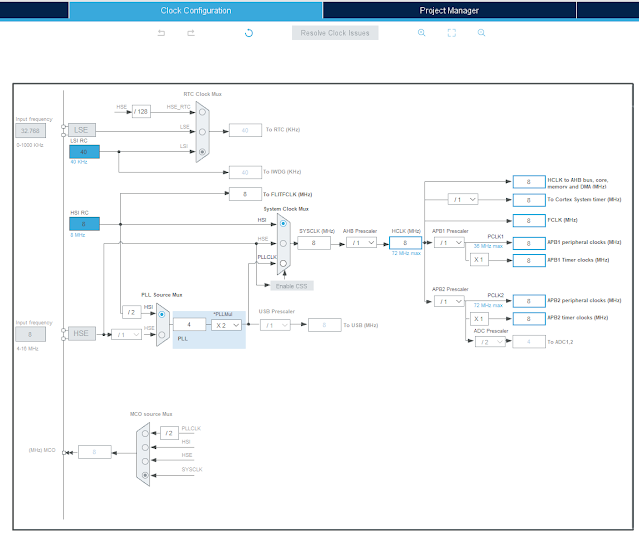
I use its internal HSI RC clock source. However this module has an external 8MHz crystal oscillator. Click here to download its source file.
Clock Configuration |
I re-arrange the Blue Pill model in Proteus VSM 8.15. I want to make its pin map similar to the physical hardware.
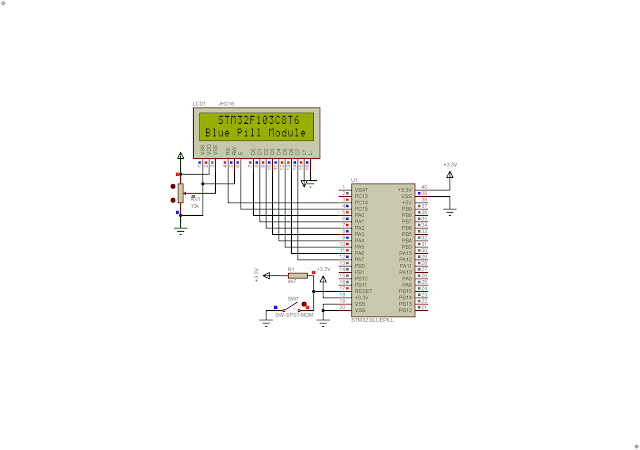 |
| Schematic Diagram |
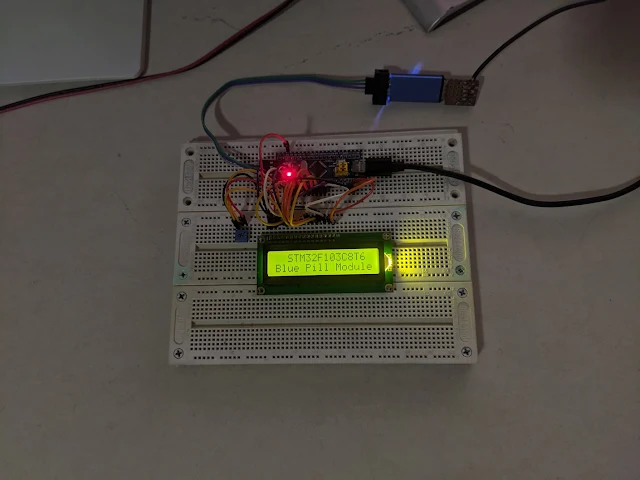 |
| Top View #1 |
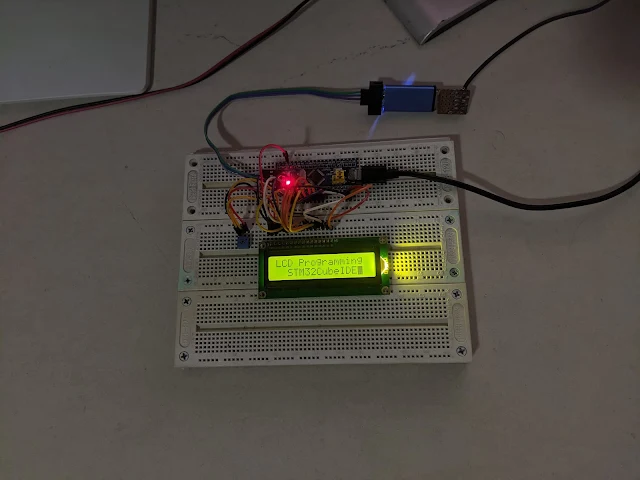 |
| Top View #2 |
However it can simulate like the original model. The STM32 Blue Pill supply voltage is +3.3V while the LCD module supply voltage is +5V. The USB power bus gives the module a stable +5V DC voltage. I use another micro USB cable connects to the USB header on the STM32 Blue Pill module.
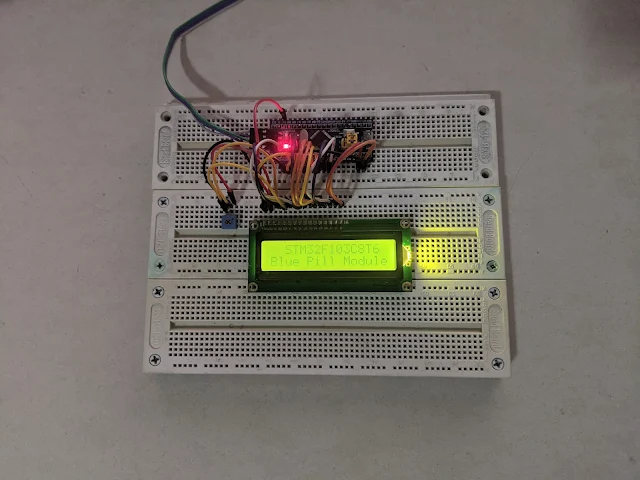 |
| Using A +3.3V Supply Voltage For The LCD Module |
However we can connect these modules to +5.0V supply voltage from the ST-LINK V2 debugger. As shown in the picture above, using a +3.3V supply for LCD module causing an insufficient power that make the display data unclear.
No comments:
Post a Comment