Overview
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is a wired synchronous serial communication interface, commonly used in embedded electronics control system used for communication between controller and its peripheral devices.
 |
| SPI Example with the SN74HC595N Shift Registers Chip |
Typical applications include interfacing micro-controllers with peripheral chips for Secure Digital cards, liquid crystal displays, analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog converters, flash and EEPROM memory, and various communication chips.
 |
| SPI Master Multiple Slave Devices Diagram |
- SCK - Serial Clock
- MOSI - Master Out Slave In
- MISO - Master In Slave Out
- CS - Chip Select
These symbol commonly used for the AVR micro-controller from Microchip Technology. However the Microchip PIC micro-controllers use different symbols.
PIC16F887 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
The PIC16F887 has a Master Synchronous Serial Port (MSSP) Module that contains the SPI and I2C module. The communication configuration depends on software setting in program.
The SPI pins locate at,
- RC3 - Serial Clock (SCK)
- RC4 - Serial Data In (SDI)
- RC5 - Serial Data Out (SDO)
- nSS - Slave Select (RA5)
The SPI operation could be configured as master or slave mode.
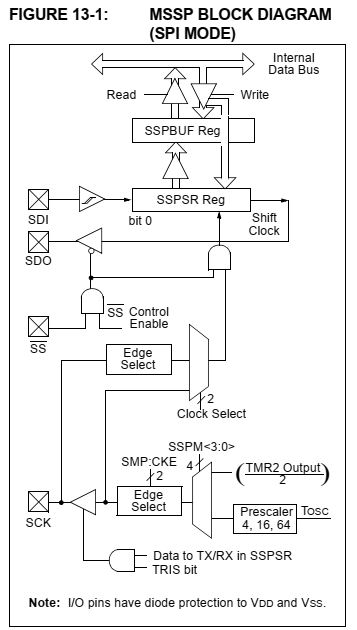 |
| MSSP Block Diagram (SPI Mode) |
To operate in master mode, the SCK, SDO and SS pin must configured as digital output pins. The SDI pin must be configured as digital input pin. The SPI operation relates to these SFR registers.
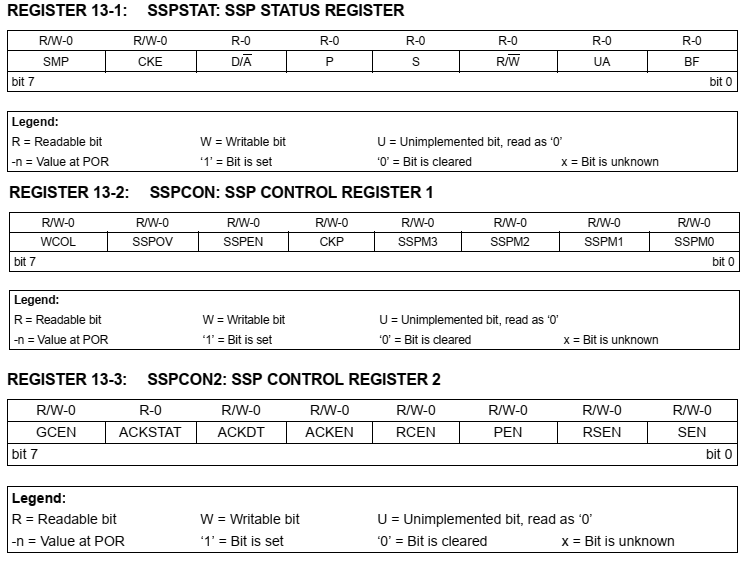 |
| MSSP Registers |
The SSPBUF is an 8-bit readable/writable register for data transmitting and receiving. The programmer must set the following configuration to operate the SPI master mode.
- Set serial clock polarity and data sample mode
- Set the SPI clock frequency
- Set the SPI I/O pins direction
- Enable the SPI module
In master mode we can select various SPI wave forms.
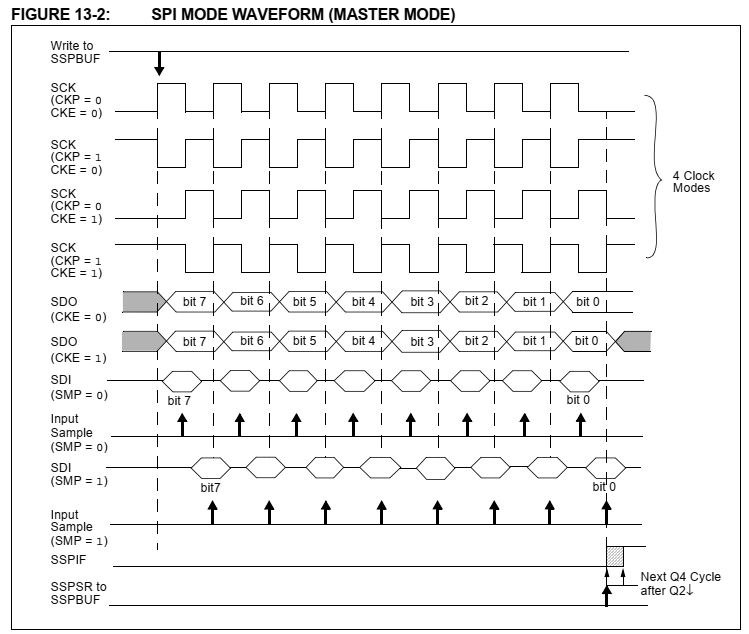 |
| SPI Master Mode Wave Form |
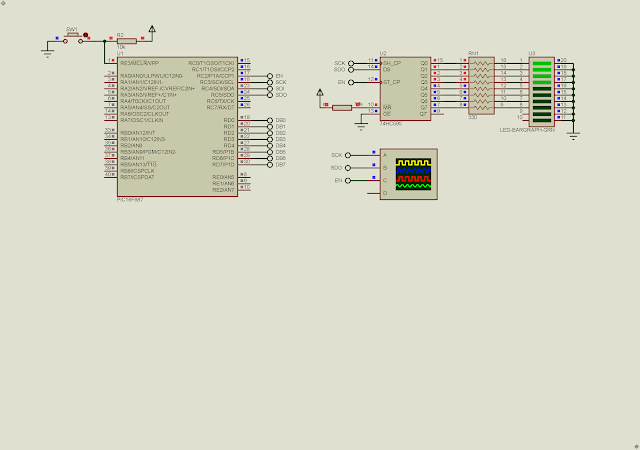
The SN74HC595N Shift Registers Interfacing Example
In this example, I use the SN74HC595N serial in parallel out shift registers to interface with the master SPI module of PIC1F887. The SN74HC595N operate as a SPI slave device receiving the data from the master.
 |
| SN74HC595N DIP-16 |
The clock transition is positive edge (low to high). The latch (slave select) pin is a high to low transition.
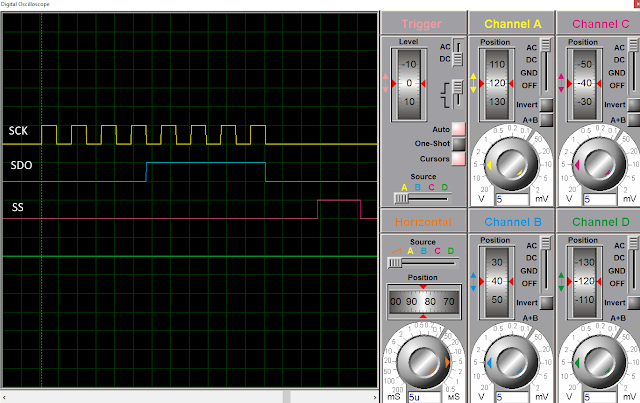 |
| SPI Wave Form |
We can serially connect these chips as much as possible. This chip is very popular in driving seven segment display or dot matrix display.
In this example, the PIC16F887 master SPI will send an 8-bit data to the SN74HC595N periodically.
Click here to download this example.
No comments:
Post a Comment