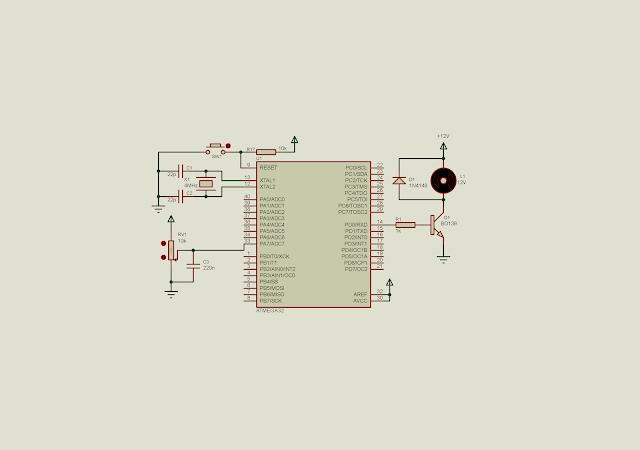
In this module we have discuss about using ADC with some typical applications. Using a POT we can adjust the analog value fed to the ADC input pin manually and linearly. With this advantage we can use the ADC value to adjust the duty cycle of PWM signal.
In this example, I use ADC to vary the PWM duty cycle between 0 to 100%. The ADC value is scaled from 1024 to 100 to fit the PWM timing. PWM signal is created by timer 0 interrupt. Each interrupt occurs for every 10 micro seconds.
Schematic diagram |
Source code:
Click here to download its source file. Back to main tutorial page ATMega32 tutorials in C with Atmel Studio 7.
No comments:
Post a Comment